| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- data_structure
- class_template
- 5397
- qsort
- 예제
- STL
- 총정리
- deletion
- Pair
- 구현
- 알고리즘
- 자료구조
- function_template
- list
- sstream
- Algorithm
- Critical_Path_Analysis
- sort
- Biconnected_Component
- 백준
- 13305
- '0'
- template
- red-black tree
- singly Linked List
- connected_component
- 문법
- c++
- Articulation_Point
- Heap
- Today
- Total
- Today
- Total
- 방명록
어제의 나보다 성장한 오늘의 나
[Algorithm] [Graph - Shortest path] (1) Single source shortest path 본문
[Algorithm] [Graph - Shortest path] (1) Single source shortest path
today_me 2022. 5. 18. 21:19이번 포스팅에서는 자료 구조 Graph를 이용 하여 Shortest Path를 찾는 방법에 대해서 알아 보려고 한다.
Shortest Path 의 특성들
◎ shorest path는 shorest subpaths 들로 구성되어 있다. (optimal substructure)
◎ cycle을 포함 하지 않는다.
크게 Single-source shortest path 와 All-pairs shortest-paths 로 나누었다.
single-source shortest path : 주어진 source vertex에서 Graph 내의 모든 vertex 까지의 가장 가까운 거리
All-pairs shortest-paths : 모든 vertex u에 대하여 u 에서 v로 가는 shortest path
Single-source shortest path 해결 방법 3가지
1) Bellman-Ford algorithm
2) In DAG
3) Dijkstra's algorithm
All-pairs shortest-paths 해결 방법
● Floyd-warshall algorithm
Single-source Shortest Path
Base
d[v] : vertex v 까지의 거리
ㅠ[v] : v의 predecessor
초기화
모든 d[v] 는 무한대로 , ㅠ[v]는 NIL로 초기화
source vertex를 s 라고 하면 d[s] = 0 으로 초기화
Relaxation 을 이용할 것이다.
Relaxation : 만약 새로운 길이 더 적게 걸린다면 그 길로 업데이트 하는 것
Relax(u,v,w){
if(d[v] > d[u] + w)
then d[v] = d[u]+w;
ㅠ[v] = u;
}

Single -source -shortest path 해결 방법
1) Bellman-Ford algorithm
◎ negative edge가 있어도 풀 수 있다.
◎ 속도가 느린편이다.
시간 복잡도
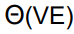
알고리듬
초기화를 진행 한다.
모든 edge들에 대하여 relaxation을 진행한다.
edge들의 순서는 관계 없다.
노드의 갯수 -1 번 반복한다.
Code

For 문을 v-1 번 반복한다. 이것은 노드의 갯수 -1 번을 의미한다.
모든 edge에 대하여 relax를 진행한다.
5~7번 줄은 test 하는 코드이다.
만약 if에 걸리게 된다면 shortest path를 제대로 찾지 못한 것이므로 False를 return 한다.
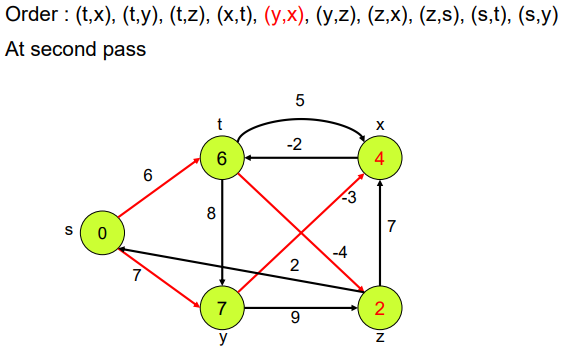
Example
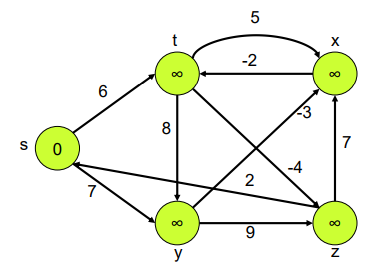
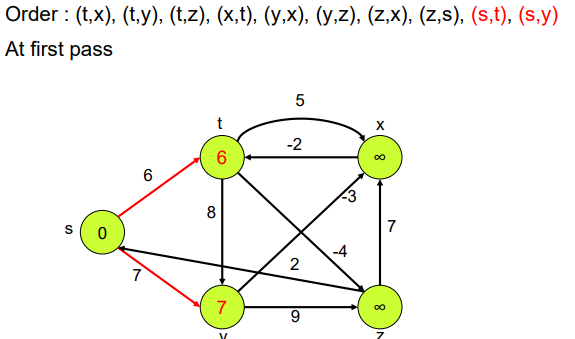
왜 모든 edge에 대하여 Relaxation을 진행 한다고 했는데 (s,t) 와 (s,y) 만 relaxation이 진행 됐나 의심이 들 수 있다.
그 이유는 다른 edge들은 Relaxation을 할 조건(d[v] > d[u]+ w)이 충족 되지 않아서 그렇다.

2) topological sort in DAG
◎ Cycle 이 없어야 가능 하다.
◎ Bellman-Ford 보다 빠르다.
◎ DAG 에서만 가능 하다.
알고리듬
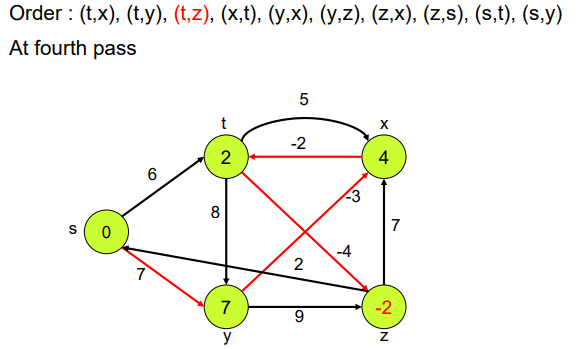
topological sort를 진행 한다.
그리고 진행한 방향으로 한번만 Relaxation을 하면 된다.
시간복잡도
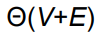
topological sort (세타(V+E)) + 초기화 (세타(V)) + Relaxation (세타(E))
Example

3. Dijkstra's Algorithm
◎ Negative edge가 없어야 함
◎ Bellman-Ford 보다 빠르다.
◎ priority queue 사용
알고리듬
초기화를 진행한다.
가장 작은 값을 꺼내 자신과 연결된 모든 vertex들을 Relaxation 한다.
그리고 그 값은 Q에서 빼서 S에 넣는다.
그리고 다시 또 가장 작은 값을 꺼내 연결된 모든 vertex들을 relaxation한다.
이것을 반복한다.
시간 복잡도
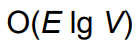
Code

S는 shortest-path가 정해진 vertex 집합
Q는 V - S 집합 (V는 전체 vertices)
Q는 priority queue 성질을 가지고 있다.
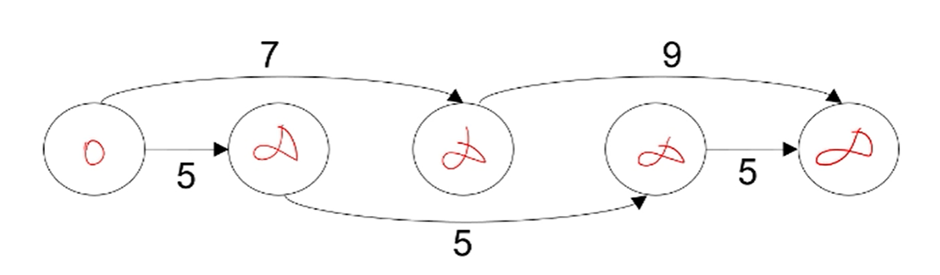
Example
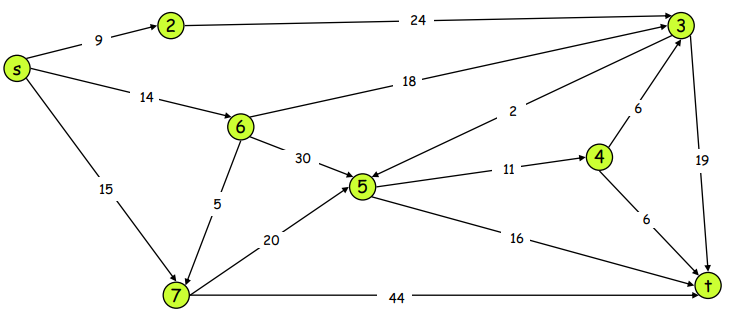
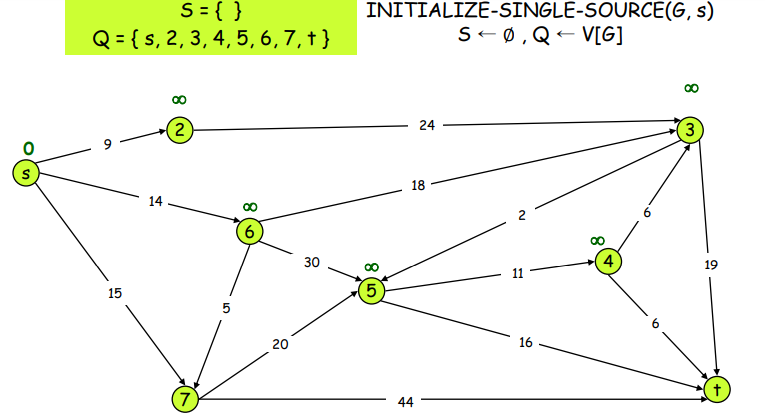

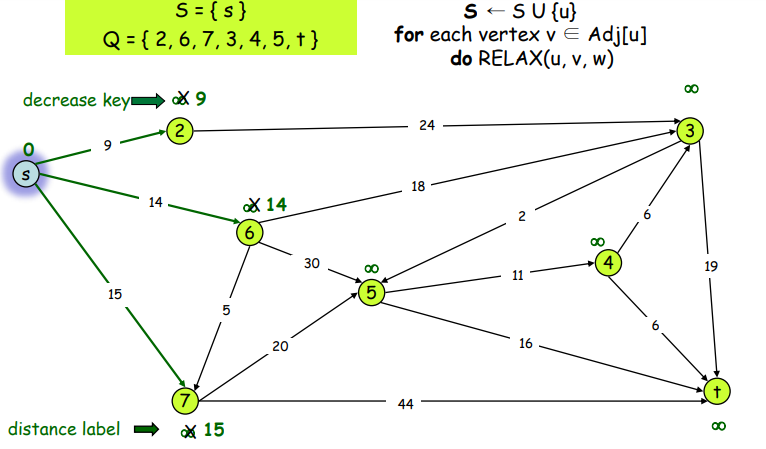




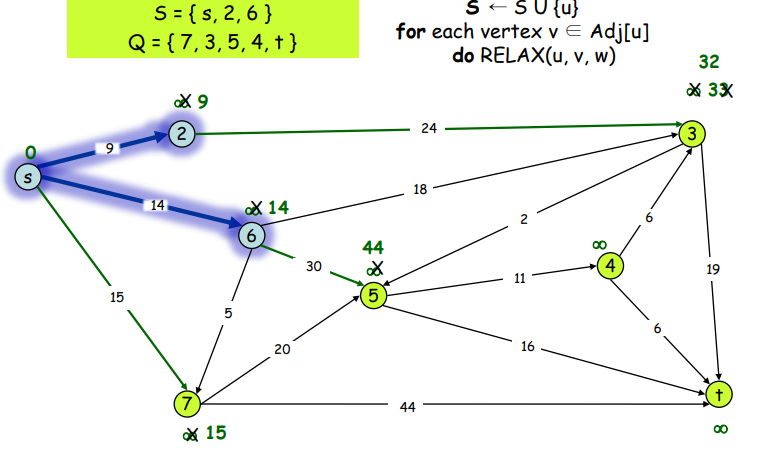
이런 식으로 계속 진행 하면 정답은

'Algorithm_Analysis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm][Sort] Counting sort( 계수 정렬 ) 총 정리 및 예제 (0) | 2022.05.27 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] Minimum Spanning Tree(MST) , Kruskal's algorithm , Prim's algorithm 총 정리 및 예제 (0) | 2022.05.18 |
| [Algorithm] DFS 의 응용 사례(Topological sort , connected components , articulation point ... 등등) (0) | 2022.05.15 |
| [Algorithm] BFS 와 DFS (0) | 2022.05.15 |
| [Algorithm_analysis] Graph 용어 정리(Graph , tree , spanning..etc) (0) | 2022.05.15 |




